Indoor air quality (IAQ) is a hot topic these days, and for good reason. With the average person spending 90% of their time indoors, the quality of that air significantly impacts our health and comfort. One key player in maintaining fresh, clean air is house ventilation. Proper ventilation can mean the difference between breathing easily or struggling with allergies and respiratory issues. Let’s dive into this essential aspect of home design that influences your well-being and enhances overall energy efficiency.
Understanding the Basics of House-Ventilation
House-Ventilation circulates fresh air throughout your living space while removing stale air. It’s essential for maintaining a healthy indoor environment. Good ventilation helps regulate temperature, reduce humidity, and keep harmful pollutants at bay.
There are two primary types of House-Ventilation: natural and mechanical. Natural ventilation relies on wind and temperature differences to move air through windows, vents, or openings. On the other hand, mechanical systems use fans and ducts to control airflow more efficiently.
Understanding how your home is ventilated is crucial for optimizing indoor air quality. When designed correctly, a balanced system ensures that you’re not just exchanging dirty air but actively improving the conditions within your home. This foundation sets the stage for healthier living spaces tailored to your needs.
The Role of Ventilation in Maintaining IAQ
Ventilation plays a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality (IAQ). By facilitating the exchange of stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air, ventilation systems help dilute pollutants. This exchange is essential for reducing concentrations of harmful substances.
Indoor spaces can quickly become trapped with contaminants like dust, smoke, and allergens without adequate ventilation. These pollutants affect comfort and can lead to health issues over time. Proper airflow helps keep these particles moving out rather than settling in your living space.
Moreover, adequate ventilation assists in controlling humidity levels. High humidity can foster mould growth and exacerbate respiratory problems. Ensuring your home has a reliable ventilation system is critical to creating a healthier indoor environment.
Types of Heat Exchange Systems: Natural vs. Mechanical
Natural heat exchange system rely on passive airflow to maintain comfortable indoor conditions. They utilize windows, vents, and the natural buoyancy of warm air rising to facilitate ventilation. This method is energy-efficient but often less predictable in terms of performance.
On the other hand, mechanical exchange systems actively control airflow through fans and ducts. These systems are more reliable because they can be adjusted according to specific needs. They can filter outdoor air for pollutants, ensuring a cleaner environment inside your home.
Both types have pros and cons depending on the climate and building design. Natural ventilation may save energy costs but could struggle during extreme weather conditions. Mechanical systems offer consistent comfort but might increase energy usage if not appropriately managed.
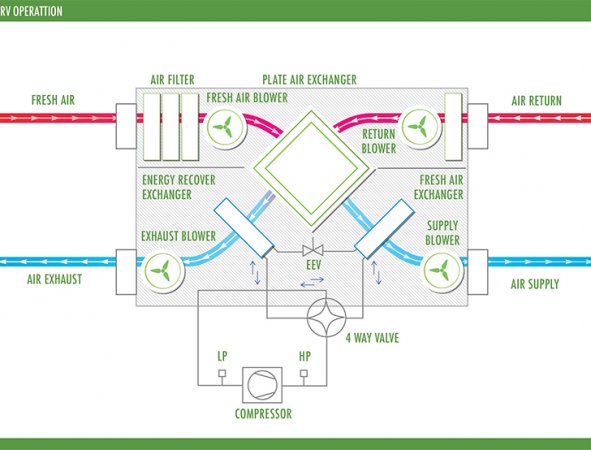
How does a Passive House Ventilation System work?
A Passive House Ventilation System operates on the principle of providing fresh air while conserving energy. It utilizes a heat recovery ventilator (HRV) or an energy recovery ventilator (ERV) to efficiently exchange indoor and outdoor air. As stale indoor air is expelled, fresh outdoor air enters through a controlled process, maintaining optimal airflow without sacrificing comfort.
The magic lies in its ability to recover heat from outgoing air before it exits the building. This means that even in cold weather, incoming air is pre-warmed, reducing the need for additional heating sources.
This balanced approach ensures consistent temperature control throughout your home while minimizing energy consumption. A Passive House-Ventilation system keeps indoor environments healthy and comfortable all year round by relying on natural pressure differences and strategically placed vents.
Identifying Common Indoor Air Pollutants
Indoor air pollutants can significantly affect your health and well-being. Common culprits include dust mites, mould spores, pet dander, and pollen. These allergens thrive in homes with poor ventilation and humidity control.
Chemical pollutants also threaten indoor air quality. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) often come from household products like paints, cleaners, and furnishings. Even new carpets release these harmful gases into the air.
Another primary concern is carbon monoxide, which can result from malfunctioning appliances or inadequate ventilation systems. It’s colourless and odourless but extremely dangerous at high levels. Regular checks on your home’s ventilation system can help mitigate exposure to these pollutants for a healthier living environment.
The Impact of Humidity Levels on IAQ
Humidity plays a crucial role in indoor air quality (IAQ). When humidity levels are too high, mould and dust mites thrive. These allergens can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems. Maintaining the right humidity balance is key for optimal IAQ.
Conversely, low humidity can also pose risks. It may dry out your skin and irritate the respiratory system, making you more susceptible to colds and flu. Dry air can also aggravate existing conditions like asthma.
Monitoring indoor humidity is essential for creating a healthy living space. Relative humidity should be between 30% and 50%. This range enhances comfort and minimizes potential pollutants that harm your home’s air quality.
Optimizing Passive House Heat Exchanger Efficiency
Optimizing the efficiency of a passive house heat exchanger is crucial for maintaining indoor comfort while minimizing energy use. Properly sizing the system meets your home’s needs, balancing airflow with heating and cooling demands. This tailored approach prevents overworking the unit, which can lead to increased wear and higher energy bills.
Regular maintenance significantly enhances performance. Cleaning filters and ensuring ductwork remains unobstructed allows for smooth airflow, maximizing heat recovery rates. It’s also essential to check seals around windows and doors to prevent leaks.
Additionally, integrating smart controls can elevate efficiency further. These systems allow you to monitor air quality in real time and adjust settings automatically based on external conditions or occupancy levels, ensuring optimal performance without unnecessary energy consumption.
How Ventilation Influences Odor Control
Proper ventilation plays a crucial role in controlling odours in your home. Stagnant air can trap unpleasant smells, making them linger longer than necessary. By ensuring fresh air circulates throughout the spaces, you can significantly diminish these odours.
Adequate House-Ventilation reduces moisture levels, often contributing to musty or mouldy scents. By replacing stale indoor air with cleaner outdoor air, you not only enhance the ambience of your home but also improve overall indoor air quality.
Moreover, ventilating specific areas like kitchens and bathrooms helps promptly remove cooking aromas and hygiene-related odours. Installing exhaust fans or opening windows during activities that produce strong smells can make a noticeable difference in how your living space feels and smells daily.
Heat Exchange System For Home: A Sustainable Solution
Heat Exchange System For Home are an innovative solution for enhancing House-Ventilation while prioritizing energy efficiency. These systems transfer heat from outgoing stale air to incoming fresh air, maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures without excessive energy consumption. This process reduces heating and cooling costs and helps minimize the carbon footprint.
A heat-exchange system can significantly improve indoor air quality by ensuring a steady fresh air flow. This continuous circulation keeps pollutants at bay and combats humidity levels that could foster mould growth or other moisture-related issues.
Moreover, these systems often feature filtration mechanisms that capture airborne particles, further contributing to healthier living environments.
Assessing the Impact of Ventilation on Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are common indoor air pollutants found in paints, cleaners, and adhesives. When inhaled over time, these compounds can evaporate into the air, leading to potential health risks. Effective House-Ventilation plays a crucial role in reducing VOC concentrations indoors.
When ventilation is optimized, stale air laden with VOCs is replaced by fresh outdoor air. This exchange dilutes harmful levels of these chemicals and helps maintain better indoor air quality. Natural ventilation through windows or vents can be adequate but may only sometimes suffice depending on environmental conditions.
Benefits of House Heat Exchanger for Respiratory Health
House heat exchanger play a significant role in promoting respiratory health.
Improved Indoor Air Quality
Discuss how heat exchangers continuously bring in fresh outdoor air while filtering out pollutants, allergens, and contaminants, leading to cleaner air for respiratory health.
Humidity Control for Comfort
Highlighting how heat exchangers help maintain optimal humidity levels in the home, preventing excessive dryness or moisture that can irritate respiratory conditions such as asthma or allergies.
Reduction of Allergens and Pollutants
Exploring how these systems effectively remove airborne allergens, dust, and other pollutants creates a healthier living environment and reduces respiratory risk.
Energy Efficiency and Consistent Temperature
They emphasise how heat exchangers improve energy efficiency by recovering heat from exhaust air, leading to a stable indoor temperature that can contribute to overall comfort and health.
How Ventilation Affects Energy Efficiency and IAQ
House-Ventilation is crucial in energy efficiency and indoor air quality (IAQ). Proper ventilation helps regulate temperature, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. When your home is well-ventilated, it maintains a comfortable environment using less energy.
Moreover, effective ventilation systems can filter out pollutants and allergens from the air. This not only improves IAQ but also reduces the strain on HVAC systems. A cleaner airflow allows these systems to operate more efficiently, lowering energy bills.
Inadequate ventilation can lead to stale air and increased humidity levels. This makes it harder for your heating or cooling units to maintain desired temperatures. As a result, you may see higher energy consumption alongside poor indoor air quality, which affects health and comfort.
The Role of Heat Exchange Ventilation in Indoor Air Quality
Heat exchange ventilation plays a crucial role in enhancing indoor air quality. It transfers heat between incoming and outgoing air, ensuring your home stays comfortable while minimizing energy loss. This system not only regulates temperature but also helps to filter out pollutants.
Fresh air enters the home and passes through filters that capture dust, allergens, and other harmful particles. As a result, you breathe cleaner air daily. The process reduces the concentration of indoor contaminants without compromising thermal comfort.
Moreover, heat-exchange systems effectively manage humidity levels. Balancing moisture content indoors prevents mould growth and mitigates odours linked to poor ventilation. This ensures a healthier living environment for everyone in the household while promoting overall well-being.
Conclusion
House ventilation plays a crucial role in shaping the quality of indoor air. Proper airflow helps to dilute pollutants, allowing for a healthier living environment. The right ventilation system can significantly impact your comfort and overall well-being. Understanding how different systems work enables homeowners to make informed decisions. Whether you choose natural or mechanical options, each has unique benefits that contribute to reducing harmful substances indoors.
FAQs
What are the signs I need better house-ventilation?
Signs of poor ventilation include persistent odours, excessive humidity or condensation on windows, mould growth, and an increase in residents’ allergy symptoms.
How often should I ventilate my home?
It’s advisable to ventilate your home regularly—ideally every day for at least 15-30 minutes. This ensures fresh air circulation and helps reduce indoor pollutants.
Can house ventilation help with energy efficiency?
Yes! Properly designed house ventilation systems can enhance energy efficiency by minimizing the need for heating and cooling while ensuring a steady supply of clean air indoors.