Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can affect individuals of all ages, leading to a range of symptoms from mild to severe. Understanding the nature of pneumonia, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing this potentially life-threatening condition. In this blog, we’ll explore what pneumonia is and discuss the role of levofloxacin, a powerful antibiotic, in treating it, including the recommended dosages.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. These air sacs, known as alveoli, may fill with fluid or pus, causing symptoms such as cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. The severity of pneumonia can vary from mild to life-threatening, and it is particularly dangerous for infants, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems or chronic health conditions.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and, less commonly, parasites. The most common types of pneumonia include:
- Bacterial Pneumonia: Often caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, bacterial pneumonia can occur on its own or after a cold or flu. It is generally more severe than viral pneumonia and can affect one or both lungs.
- Viral Pneumonia: Viruses that cause colds and flu can also cause pneumonia. Viral pneumonia is usually less severe than bacterial pneumonia but can still be serious, especially in young children and the elderly.
- Fungal Pneumonia: Fungal pneumonia is less common and typically affects people with weakened immune systems. Fungi that cause pneumonia can be found in soil or bird droppings.
- Aspiration Pneumonia: This type of pneumonia occurs when food, liquid, or vomit is inhaled into the lungs, leading to infection.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the type of infection, the age of the patient, and their overall health. Common symptoms include:
- Cough: Often accompanied by phlegm or mucus, the cough can be persistent and may produce yellow, green, or bloody sputum.
- Fever and Chills: A high fever, often with shaking chills, is common in pneumonia.
- Shortness of Breath: Patients may experience difficulty breathing or rapid, shallow breathing.
- Chest Pain: Sharp or stabbing chest pain that worsens with deep breaths or coughing.
- Fatigue: General weakness and fatigue are common, and in severe cases, patients may become confused or delirious.
- Sweating and Clammy Skin: Excessive sweating and clammy skin are often associated with fever.
In infants and older adults, pneumonia symptoms may be more subtle, such as low body temperature, confusion, or lethargy. It’s important to seek medical attention if pneumonia is suspected, especially in these vulnerable populations.
Diagnosing Pneumonia
To diagnose pneumonia, a healthcare provider will typically start with a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. They may listen to the lungs with a stethoscope to detect abnormal sounds such as crackling or bubbling, which can indicate the presence of fluid or infection in the lungs.
Additional diagnostic tests may include:
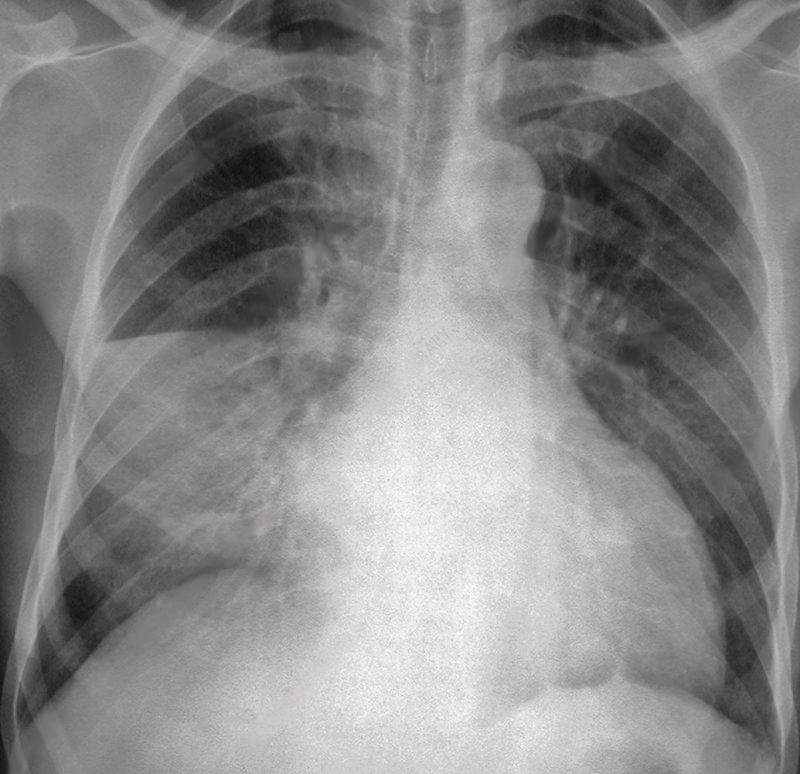
- Chest X-Ray: A chest X-ray can confirm the presence of pneumonia and show the extent and location of the infection in the lungs.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help determine the type of infection and the body’s response to it.
- Sputum Test: A sample of mucus or phlegm may be collected and analyzed to identify the specific bacteria or virus causing the infection.
- Pulse Oximetry: This test measures the oxygen level in the blood to determine how well the lungs are functioning.
Treatment of Pneumonia
The treatment of pneumonia depends on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient’s overall health. Treatment may include antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal medications, and supportive care such as rest, fluids, and oxygen therapy.
Antibiotics for Bacterial Pneumonia
For bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are the primary treatment. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection, the patient’s age, and any underlying health conditions. Levofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, is one of the commonly prescribed medications for treating bacterial pneumonia.
Levofloxacin for Pneumonia
Levofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is highly effective against a variety of bacterial pathogens, including those commonly responsible for pneumonia. It works by inhibiting bacterial DNA synthesis, which prevents the bacteria from replicating and spreading. Buy Levofloxacin Online at Medzsupplier top leading Levofloxacin Wholesaler
How Levofloxacin Works
Levofloxacin targets the bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV enzymes, which are essential for DNA replication and repair. By inhibiting these enzymes, levofloxacin disrupts the DNA processes within the bacterial cell, leading to cell death and the resolution of the infection.
Levofloxacin Dosage for Pneumonia
The dosage of levofloxacin for pneumonia depends on the severity of the infection, the patient’s age, kidney function, and whether the pneumonia is acquired in the community (community-acquired pneumonia, CAP) or in a healthcare setting (hospital-acquired pneumonia, HAP).
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP): For most adults with CAP, the recommended dosage of levofloxacin is 500 mg once daily for 7 to 14 days. In some cases, a higher dose of 750 mg once daily may be prescribed for 5 days, particularly for severe infections.
- Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia (HAP): In patients with HAP, the dosage may be adjusted based on the severity of the infection and the patient’s kidney function. Typically, 750 mg once daily for 7 to 14 days is recommended.
- Special Considerations: For patients with impaired kidney function, the dosage of levofloxacin may need to be reduced to prevent drug accumulation and potential side effects. Healthcare providers will adjust the dose based on the patient’s creatinine clearance levels.
Side Effects of Levofloxacin
While levofloxacin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some patients. Common side effects include:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting are the most common side effects.
- Central Nervous System Effects: Dizziness, headaches, and confusion may occur, particularly in older adults.
- Tendonitis and Tendon Rupture: Levofloxacin has been associated with an increased risk of tendonitis and tendon rupture, especially in patients over 60, those taking corticosteroids, and those with kidney, heart, or lung transplants.
- Photosensitivity: Patients taking levofloxacin may become more sensitive to sunlight and should avoid excessive sun exposure or use sunscreen.
Precautions and Interactions
Before taking levofloxacin, patients should inform their healthcare provider of any other medications they are taking, as levofloxacin can interact with certain drugs, including anticoagulants, antacids, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Patients with a history of tendon disorders, epilepsy, or QT prolongation should use levofloxacin with caution, as it may exacerbate these conditions.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a potentially serious infection that requires prompt and effective treatment. Levofloxacin is a powerful antibiotic that can effectively treat bacterial pneumonia, offering a convenient dosing schedule and broad-spectrum coverage against the most common pathogens. However, like all antibiotics, it should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure the best outcome and to minimize the risk of side effects and antibiotic resistance. Visit at Medzsupplier
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of pneumonia, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment with medications like levofloxacin can lead to a quicker recovery and prevent complications.